If you strip away the frameworks, libraries, and fancy UI layers, every website still depends on basic HTML. The way you structure that HTML determines how well your site performs, how accessible it is, and how easy it is to maintain over time. That’s where semantic HTML comes in.
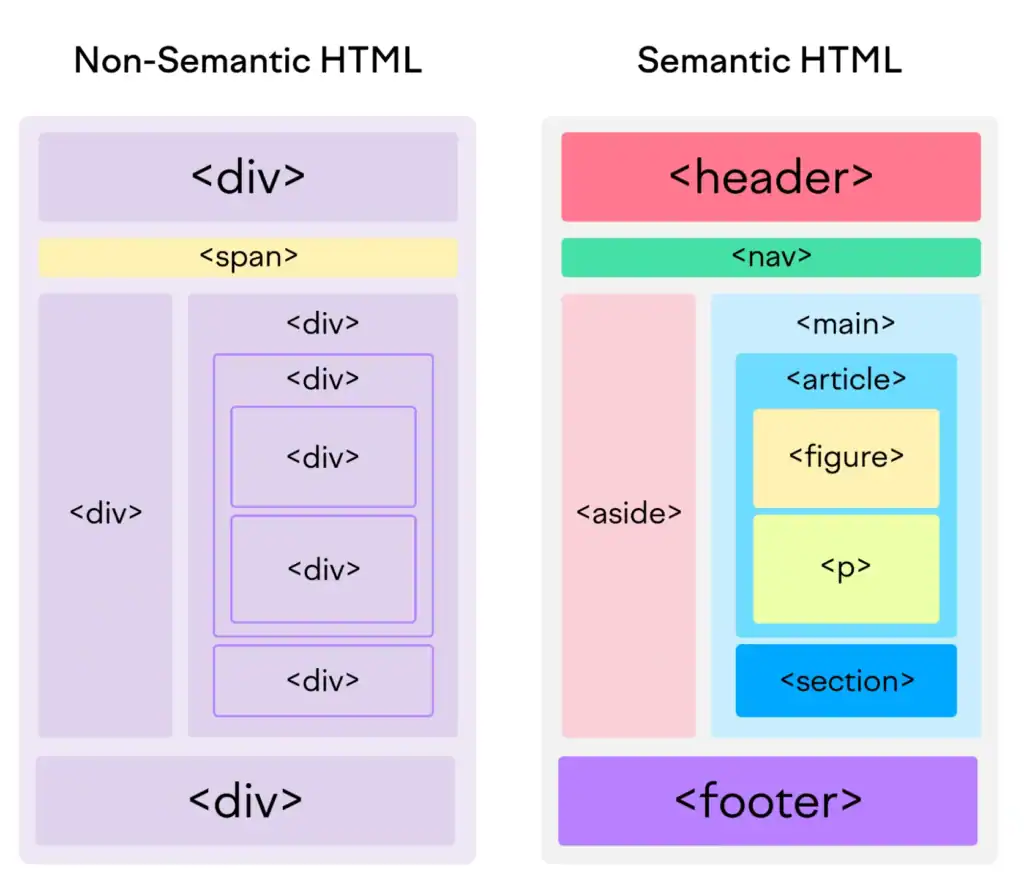
Semantic tags describe the meaning of your content. Instead of using endless divs, you use elements that communicate structure and purpose. It’s simple, but the impact is huge.
Let’s break down why semantic HTML is still one of the most valuable skills a developer can master.

1. It Builds a Clear Content Structure
Search engines and assistive technologies rely on your HTML structure to understand what your page is about.
Key tags that define structure:
headernavmainsectionarticleasidefooter
These tags create a natural hierarchy. A search engine can immediately tell where your navigation is, what your main content is, and how your page flows.
2. It Boosts Accessibility
Screen readers use semantic tags to help users navigate.
For example:
navtells screen readers “this area contains navigation links.”mainhelps them jump straight to the primary content.articlelets them skip between major topics easily.
Without semantic tags, assistive tech has to guess what your content means — and it usually guesses wrong.
3. Better SEO Without Extra Effort
Semantic HTML helps search engines understand priority and context.
For example:
articletells Google the content is standalone and important.sectiondivides topics into meaningful groups.asideindicates secondary content like notes or references.headerinside each section helps clarify the topic.
It’s free SEO that requires no plugin, no schema setup, and no extra scripts.
4. Your Code Becomes Future-Proof
A good HTML structure makes long-term maintenance far easier.
Future you — or another developer — can skim the markup and instantly understand what each part of the page does.
Compare this:
Bad:
<div class="top"></div>
<div class="big"></div>
<div class="left"></div>
Good:
<header></header>
<main></main>
<aside></aside>
One explains itself. The other creates chaos.
5. Semantic HTML Works Perfectly With Modern Frameworks
Whether you’re using React, Vue, Next.js, or plain PHP, semantic tags fit naturally into component-based structures.
A React example:
export default function BlogArticle() {
return (
<article>
<header>
<h1>Why Semantic HTML Matters</h1>
</header>
<section>
<p>Content goes here…</p>
</section>
<footer>Written by Sabbir</footer>
</article>
);
}
Good markup + good components = scalable front-end.
6. Important Semantic Tags Every Developer Should Use
Here’s a simple cheat sheet:
Page Layout
htmlbodyheadernavmainfooter
Content Grouping
sectionarticleasidefigureandfigcaption
Text Meaning
strongemmark
Forms
labelfieldsetlegend
Use them consistently and your site instantly feels more organized.
Conclusion
Semantic HTML isn’t “beginner stuff.” It’s foundational, professional web development.
It improves accessibility, strengthens SEO, creates clearer code, and makes your projects easier to scale.
If you want your work to age gracefully and function well for every user — start with the structure. Semantic HTML gives you that structure.